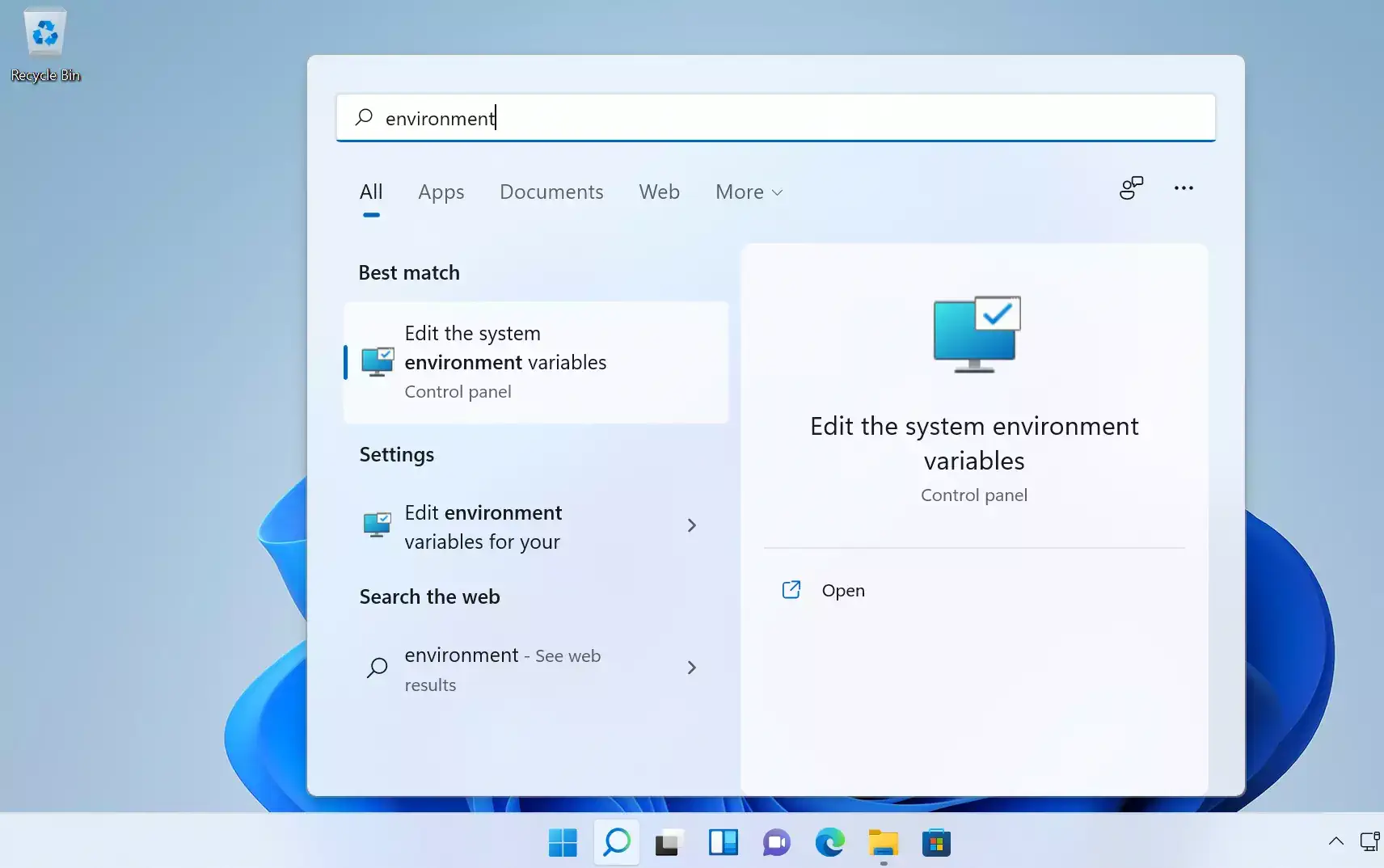
Setting up Windows environment variables can reduce the time it takes to type commands at the command line.
Environment variables on Windows are records of system folder locations, system properties and others that are accessible to any program or script.
One of the most commonly used environment variables is PATH, which indicates the folders in which files are searched for, whether called from the command line, Windows terminal, bat file or other sources.
- To open Windows environment variables, you can use the taskbar search or press “Win+R” on your keyboard and type “sysdm.cp”.
- Under the “Advanced” tab, click on “Environment variables…”.
- Under “User environment variables” or “System variables” select the variable you wish to change and click on “Change”.
- If you want to create a new variable, click on “Create”.
- To add a new value (path) to the system variable in the next window, you can either click “Create” or simply double-click on the first blank line, then enter the desired path to the folder containing the executables we want.
- You can also use the “Edit Text” button, in which case the window for changing a system variable will open differently: the name of the variable and, below it, its value. In case of specifying paths, the value will be all paths stored in the variable, separated by semicolons.
- When creating a new environment variable, the window will be the same as in the 5th step: you should specify the system variable name in the upper field and its value in the lower field.